
Above: Sandvik titanium powder plant in Sandviken/Image Credit: Sandvik Group
Sandvik’s new state-of-the art titanium powder plant and additive manufacturing operations in Sandviken recently received the prestigious ‘AS9100 Revision D’ certification for deliveries to the aerospace industry. Powders made at new state-of-the-art facility in Sweden will accelerate the adoption of 3D printed titanium parts and the shift towards sustainable manufacturing.
Excited at the certification, Keith Murray, VP Global Sales, Sandvik Additive Manufacturing said, “Having atomized fine metal powders for more than 40 years, and supplying titanium to the aerospace industry since the 1980s, Sandvik is no stranger to powder atomization or the requirements of the most demanding industries.”

Above: Powder jars of Sandvik titanium power/Image Credit: Sandvik Group
Sandvik’s powder plant for Osprey® titanium and nickel-based superalloys was inaugurated in the end of 2019 in Sandviken, Sweden, with more than 150 guests including end-users in key industries like aerospace and medical. Since then an extensive work has been ongoing to ramp-up the highly automated plant, finetuning all processes and qualifying the powder to ensure the best possible consistency, morphology and quality suitable for additive manufacturing. As a result of the meticulous and structured work, the ‘AS9100 Revision D’ certification for aerospace was recently received, in April this year. At the same time the additive manufacturing facility in Sandviken also achieved the AS9100D aerospace certification.
Keith added, “Now we are one of few metal powder and additive manufacturing companies that has the new and prestigious ‘AS 9100 Revision D’ quality certification. It is a true milestone, which will facilitate many customer collaborations going forward. Imagine what 158 years of leading materials expertise can do for your additive process.”
Driving the Shift towards Sustainable Manufacturing

Above: The additive version of CoroMill® 390 milling cutter has resulted in optimized design, 80% lower weight and up to 200% increased productivity/Image Credit: Sandvik Group
Titanium has exceptional material properties, being strong yet light and offering high levels of corrosion resistance. At the same time, it is biocompatible. However, the cost and complexity of machining from titanium billet have historically restricted its use to high value, low volume industries such as aerospace, medical and defence.
The launch of titanium powders for additive manufacturing supports a growing trend towards the 3D printing of titanium parts – and the shift towards sustainable manufacturing. The additive process results in far less material waste than traditional subtractive techniques, while also encouraging new levels of design freedom. This is opening up the use of titanium in other industries such as automotive and tooling. Sandvik’s own Lightweight CoroMill® 390 is an excellent proof of the latter, where the additive version of the mill is more than 80% lighter and up to 200% more productive.
Powder metallurgy is also labelled as a ‘recognized green technology’ – and the net-shape capability of technologies like additive manufacturing not only means that material waste is minimized, but also that great energy efficiency can be achieved, by eliminating manufacturing steps.
According to Keith Murray, “If combining this with the opportunities with a light and strong material like titanium, the sustainability advantages can be enormous. Weight reduction is for example a constant key issue for the aerospace industry, driven both by fuel cost and carbon footprint. The same is true for cars and trucks, and everything else that moves. Each kilogram of weight loss on an airplane saves about 3,000 US dollars per year in fuel – and can make a great difference for the planet.”
Incomparable level of traceability and excellent consistency
Traceability is of vital importance in the aerospace industry. Sandvik can offer an incomparable level of traceability for its titanium powder, which is made possible by having the full supply chain in-house – from titanium sponge to finished powder. The new titanium powder process uses advanced electrode inert gas atomization technology to produce highly consistent and repeatable titanium powder with low oxygen and nitrogen levels. The automated production process is also supported by several industrial robots and a dedicated downstream sieving, blending and packing facility.
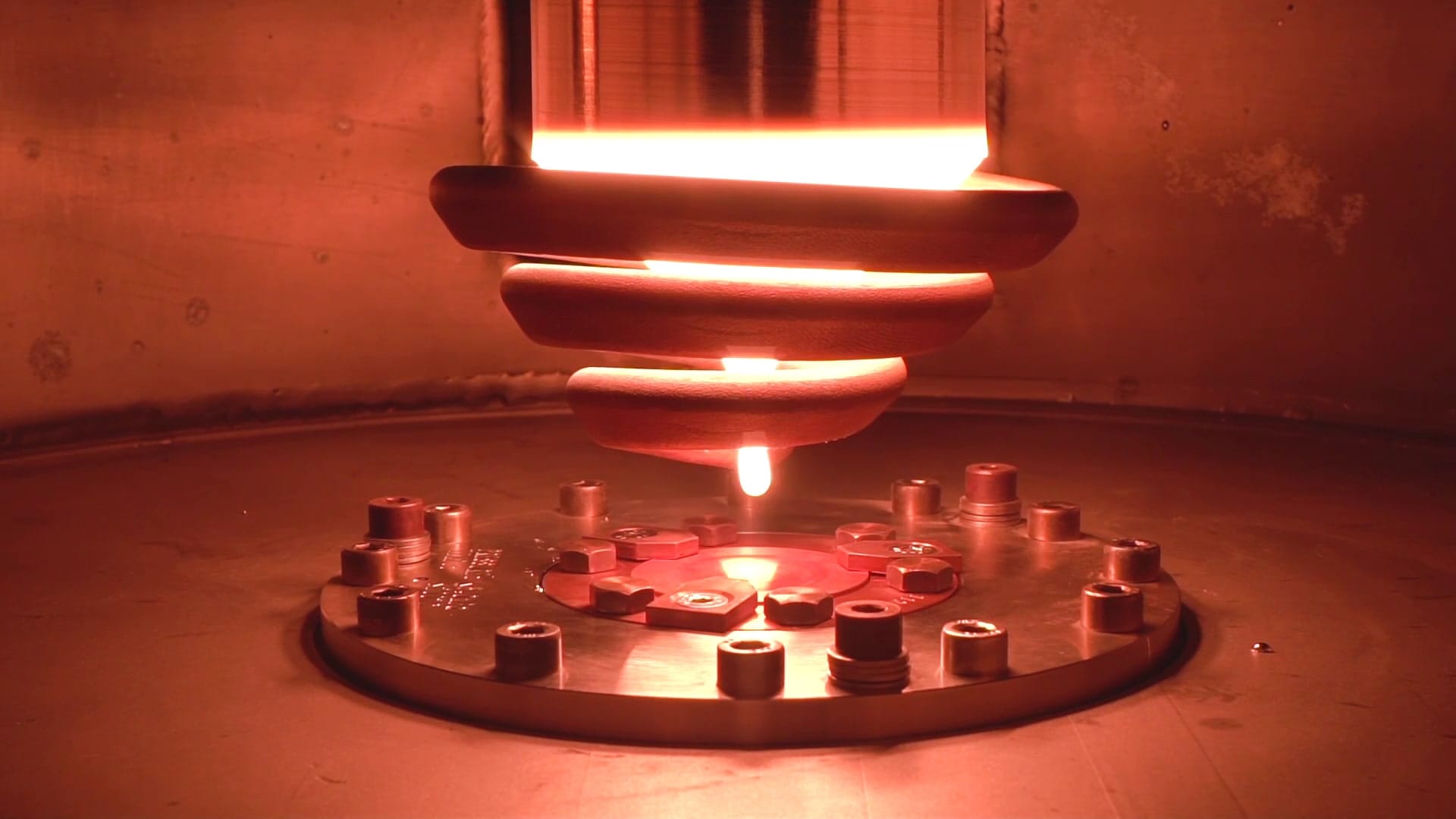
Above: Heating titanium rod at Sandvik’s new state-of-the art powder plant for titanium and nickel-based superalloys/Image Credit: Sandvik Group
Keith Murray comments, “In additive manufacturing it is essential to use high-quality metal powders with consistent quality, adapted to the different additive manufacturing processes. Our highly automated manufacturing process ensures excellent consistency – and the powders demonstrate optimal particle size distribution.”
The new powder plant for titanium and nickel-based superalloys is located in Sandviken, Sweden, just next to Sandvik’s additive manufacturing facility, which includes all relevant additive manufacturing processes for metals. This means that the company can tailor the powder to different printing processes, on the same site.

Above: Osprey® metal powder jar/Image Credit: Sandvik Group
Kristian Egeberg, President of Sandvik Additive Manufacturing concludes; “Sandvik is a world leader in metal powder for additive manufacturing with the widest alloy program on the market. Titanium powders represent the latest application of 158 years of materials knowledge and R&D – and more than 40 years in-house powder manufacturing capabilities. With the AS9100D certification together with all our experts in materials, metal powder and additive manufacturing, we can now help our customers succeed in this high-growth area.”
The first two powders produced at the plant will be Osprey® Ti-6Al-4V Grade 5 and Osprey® Ti-6Al-4V Grade 23. Other alloys are available on request. In addition to the AS9100D certification, the plant is also certified according to ISO 9001, ISO 14001 and ISO 45001.
About Manufactur3D Magazine: Manufactur3D is an online magazine on 3D Printing. Visit our Global News page for more updates on Global 3D Printing News. To stay up-to-date about the latest happenings in the 3D printing world, like us on Facebook or follow us on LinkedIn.



